European Milk Production Update – Sep ’21
Executive Summary
EU-27+UK milk production figures provided by Eurostat and the Agriculture and Horticulture Development Board of the United Kingdom were recently updated with values spanning through Jul ’21. Highlights from the updated report include:
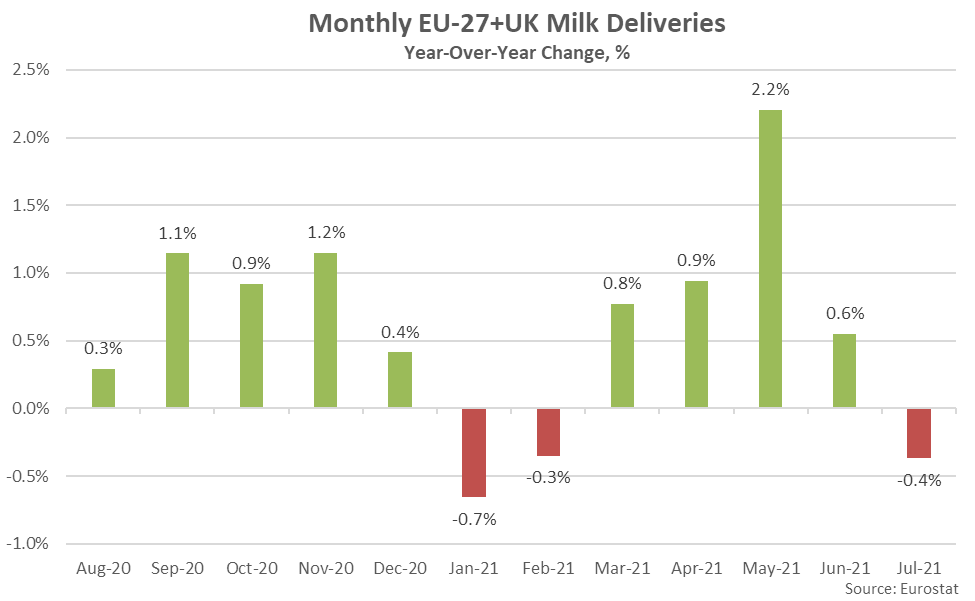
- Jul ’21 EU-27+UK milk production volumes finished 0.4% below the record high seasonal level experienced throughout the previous year. The YOY decline in EU-27+UK milk production volumes was the first experienced throughout the past five months.
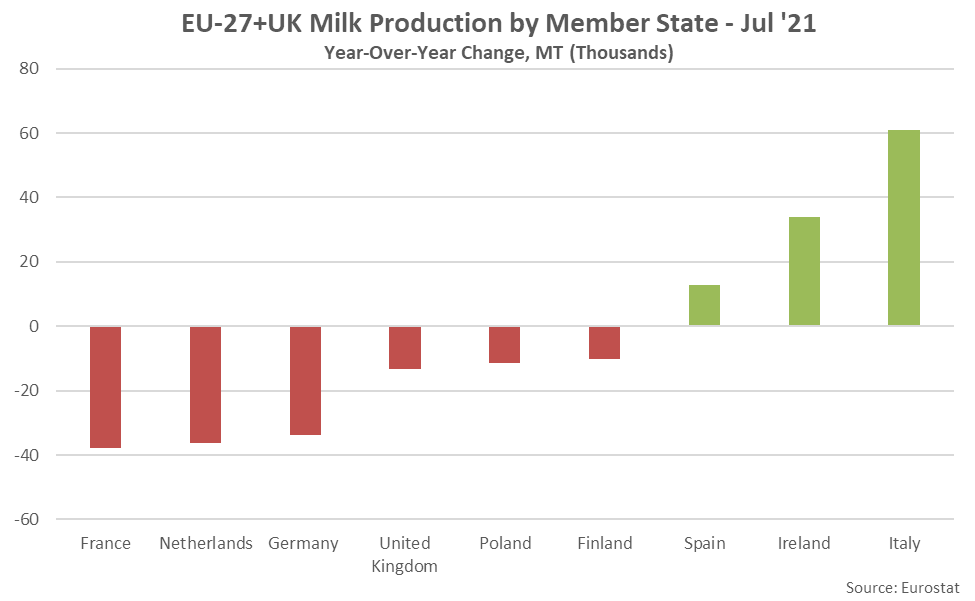
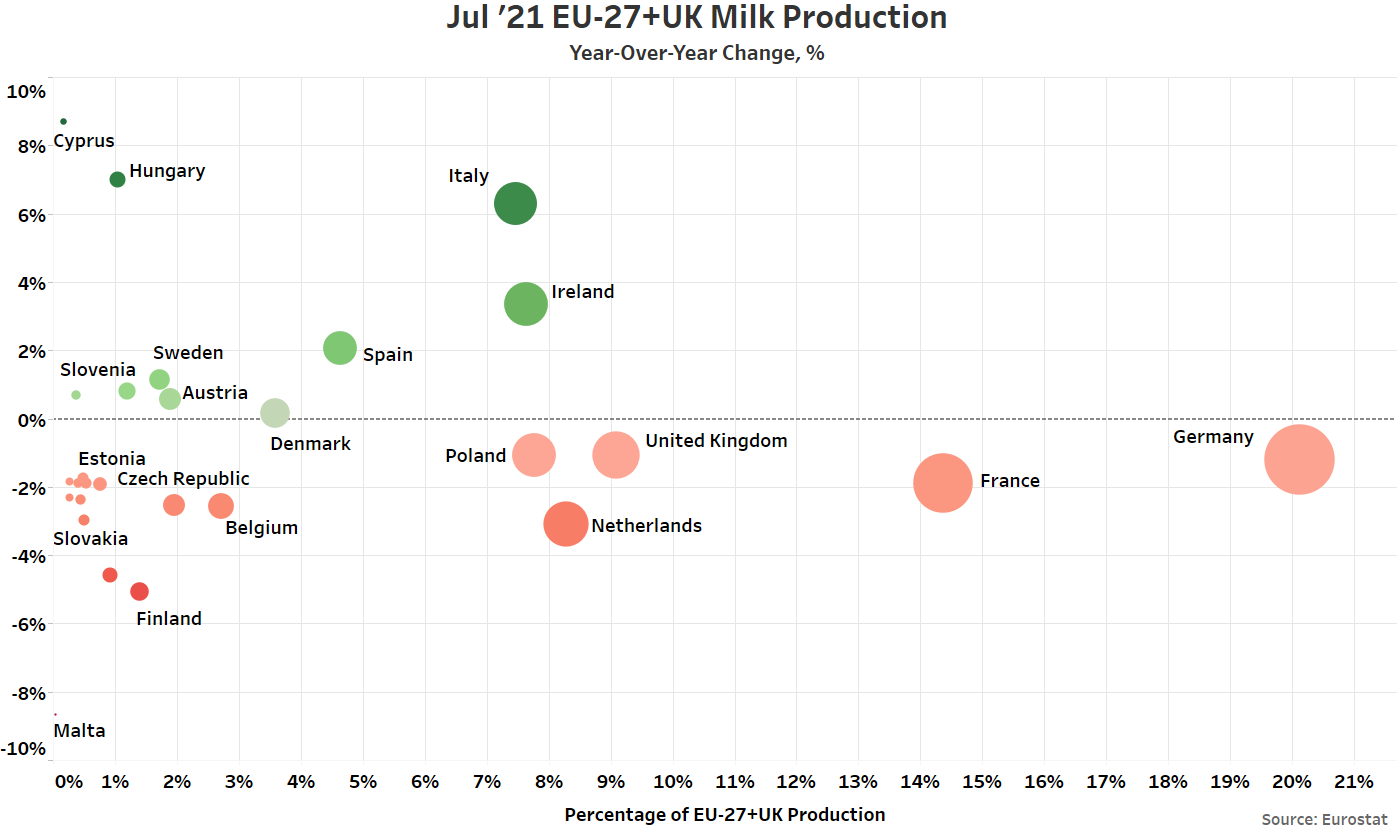
- Jul ’21 YOY declines in milk production were led by France, followed by the Netherlands and Germany, while production volumes increased most significantly from the previous year throughout Italy. Overall, 18 of the 28 countries experienced YOY declines in milk production throughout the month.
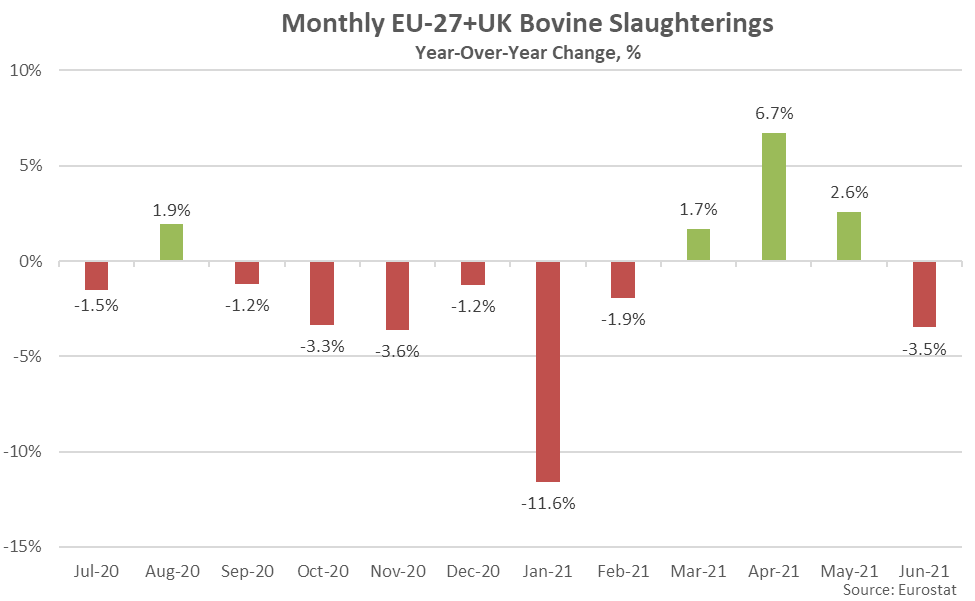
- EU-27+UK beef & dairy cow slaughter rates finished lower on a YOY basis for the first time in the past four months during Jun ’21 when normalizing for slaughter days, declining by 3.5% and reaching a seven year low seasonal level.
Additional Report Details
Milk Production
According to Eurostat and the Agriculture and Horticulture Development Board of the United Kingdom, Jul ’21 EU-27+UK milk production volumes declined seasonally to a five month low level while finishing 0.4% below the record high seasonal level experienced throughout the previous year. According to the USDA, summer heat and humidity experienced throughout much of Europe contributed to the YOY decline in milk production volumes.
Figures for Sweden and Luxembourg are not yet available and are based on the previous month YOY change in production. Sweden and Luxembourg have combined to account for just 2.0% of total EU-27+UK production volumes throughout the past 12 months.
’20-’21 annual EU-27+UK milk production volumes finished 0.6% higher on a YOY basis, reaching a record high level for the fourth consecutive year. ’21-’22 YTD EU-27+UK milk production volumes have increased by an additional 0.8% throughout the first third of the production season, despite the most recent decline.
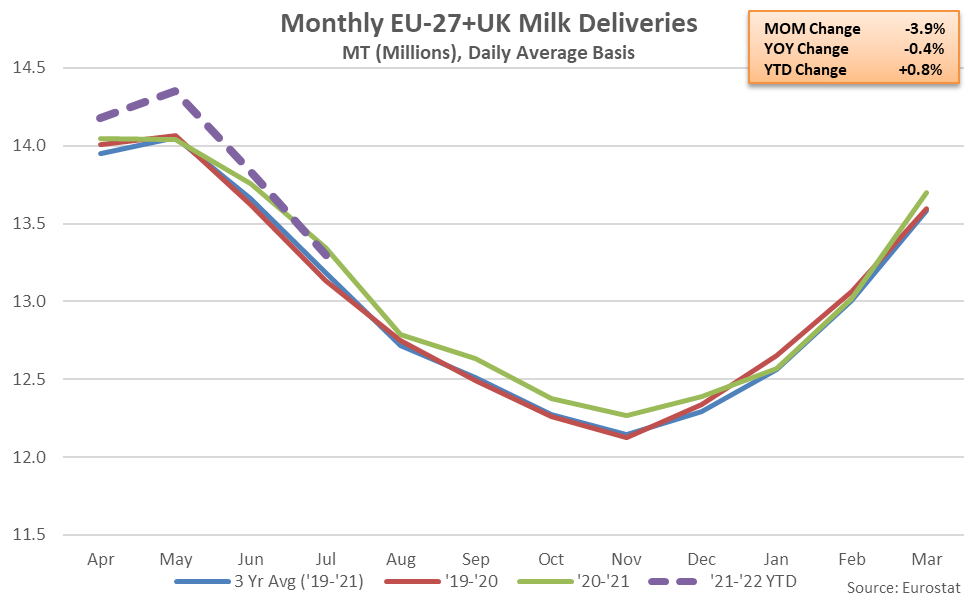
The Jul ’21 YOY decline in EU-27+UK milk production volumes was the first experienced throughout the past five months. EU-27+UK milk production volumes had finished higher on a YOY basis over 26 of the past 29 months through Jun ’21, prior to declining throughout the month of July.
Jul ’21 YOY declines in production on an absolute basis were led by France, followed by the Netherlands and Germany, while YOY increases in production on an absolute basis were led by Italy, followed by Ireland.
YOY declines in production on a percentage basis were led by Malta (-8.7%), followed by Finland (-5.1%) and Lithuania (-4.6%), while increases in production on a percentage basis were led by Cyprus (+8.7%), followed by Hungary (+7.0%) and Italy (+6.3%).
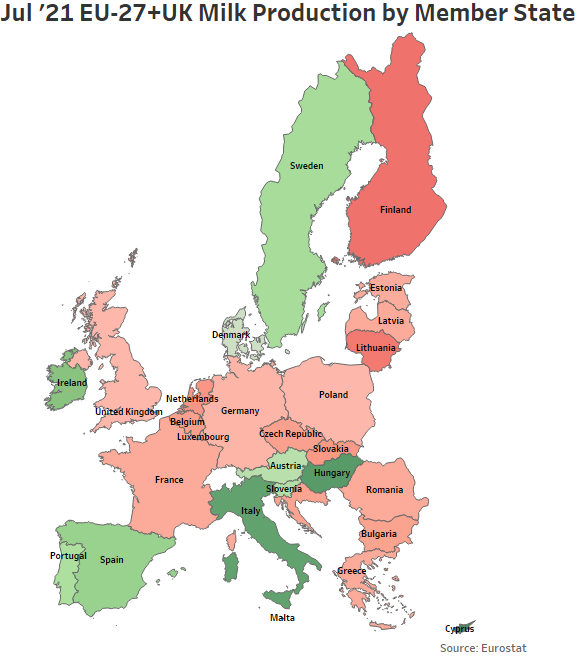
Six of the top ten milk producing member states experienced YOY declines in milk production during Jul ’21, as production within the top ten milk producing member states declined by a weighted average of 0.2% throughout the month. The top ten EU-27+UK milk producing member states accounted for over 85% of the total EU-27+UK milk production experienced throughout the month. Production outside of the top ten milk producing member states declined by 0.8% on a YOY basis. Overall, 18 of the 28 countries experienced YOY declines in production volumes during Jul ’21.
Beef & Dairy Cow Slaughter
EU-27+UK beef & dairy cow slaughter finished lower on a YOY basis for the first time in the past four months during Jun ’21 when normalizing for slaughter days, declining by 3.5% and reaching a seven year low seasonal level. YOY declines in beef & dairy cow slaughter were most significant throughout Ireland, followed by the United Kingdom and France.
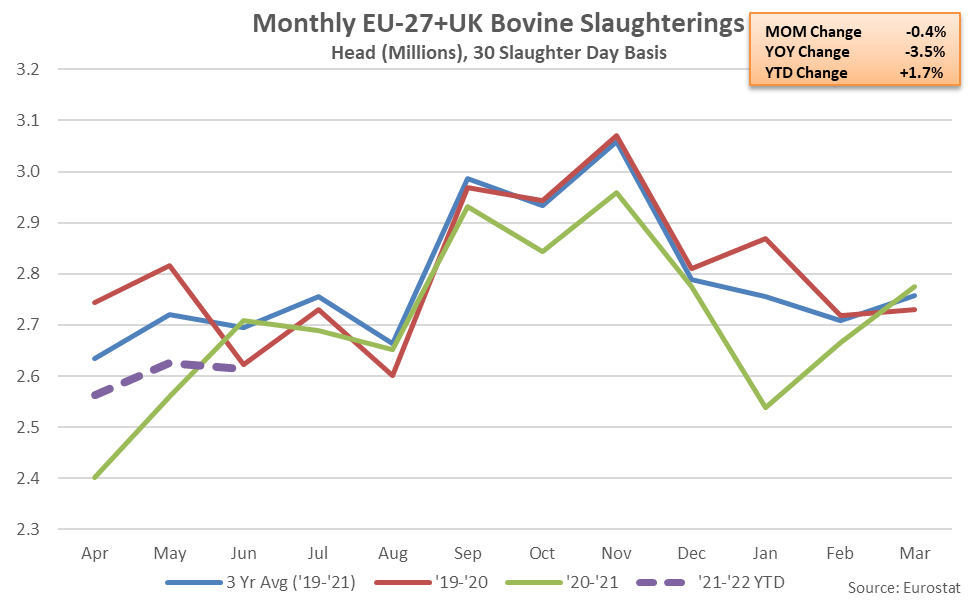
’20-’21 annual EU-27+UK bovine slaughter declined on a YOY basis for the second consecutive year, finishing down 3.3% and reaching a seven year low level. The USDA is projecting a 1.0% YOY decline in the EU-27+UK dairy cow herd throughout the 2021 calendar, following the general trend towards an overall smaller herd size and more productive animals.