Atten Babler Corn & Soybeans FX Indices – May…
Corn FX Indices:
The Atten Babler Commodities Corn Foreign Exchange (FX) Indices were mixed throughout Apr ’22. The USD/Corn Exporter FX Index declined to a five month low level however the USD/Corn Importer FX Index and USD/Domestic Corn Importer FX each reached record high levels.
Global Corn Net Trade:
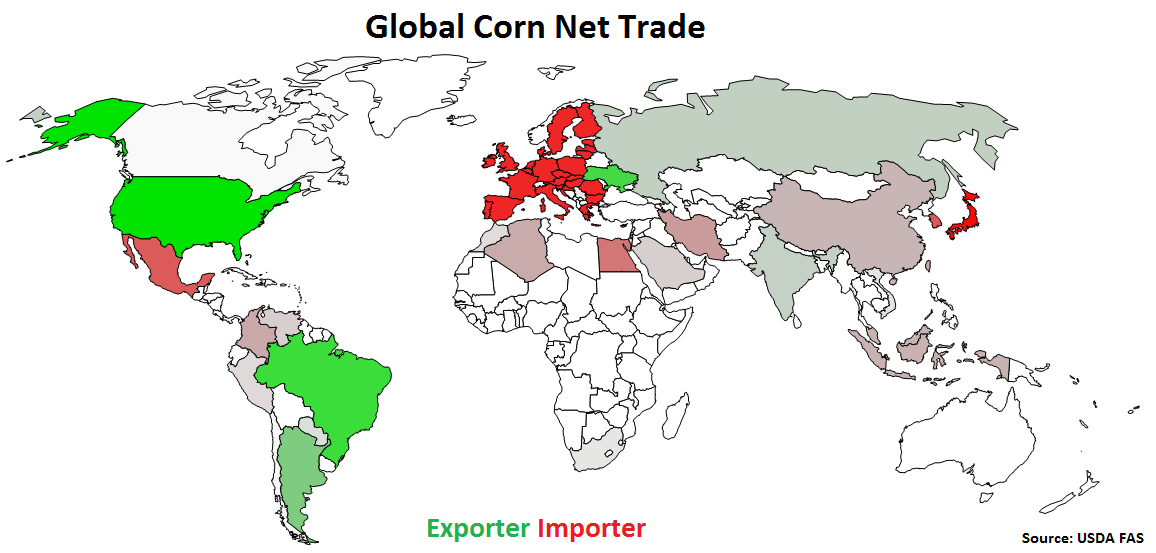
Major net corn exporters are led by the U.S., followed by Brazil, Ukraine, Argentina, Russia and India (represented in green in the chart below). Major net corn importers are led by the EU-28, followed by Japan, Mexico, South Korea, Egypt and Iran (represented in red in the chart below).
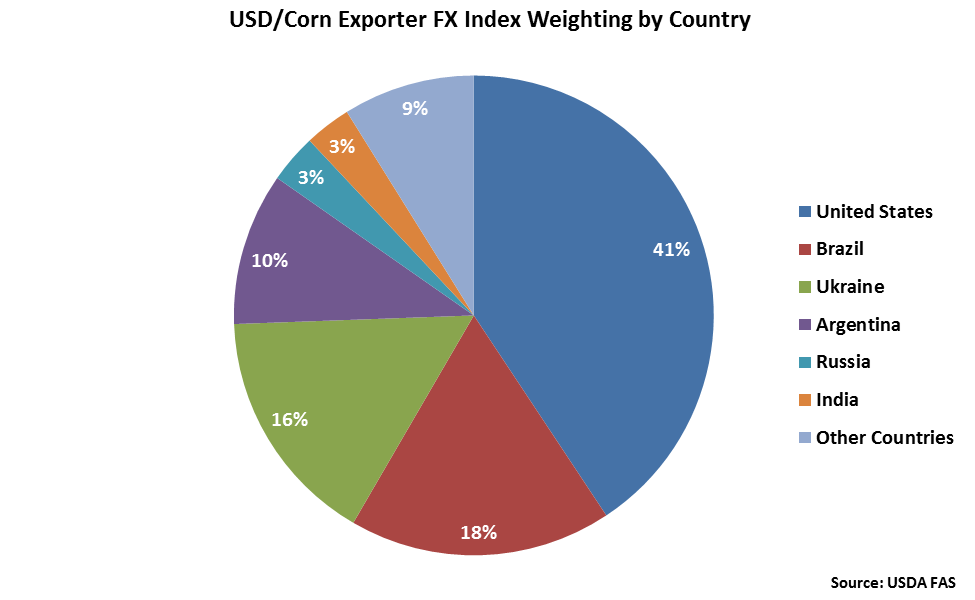
The United States accounts for over two fifths of the USD/Corn Exporter FX Index, followed by Brazil at 18%, Ukraine at 16% and Argentina at 10%.
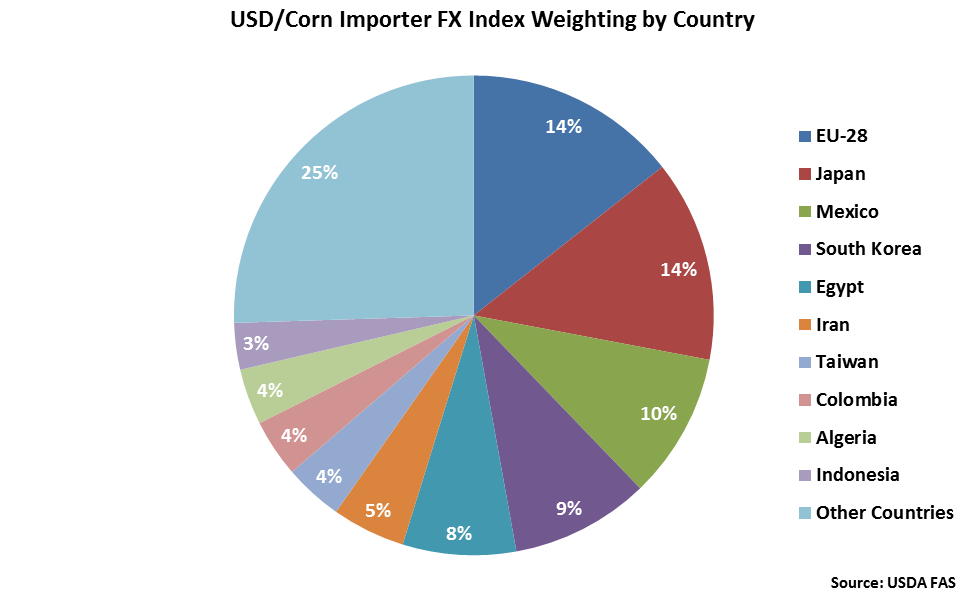
The EU-28 and Japan each account for 14% of the USD/Corn Importer FX Index. Mexico, South Korea, Egypt and Iran each account for between 5-10% of the index.
USD/Corn Exporter FX Index:
The USD/Corn Exporter FX Index declined 4.4 points throughout Apr ’22, finishing at a five month low level of 283.4. The USD/Corn Exporter FX Index remained up 3.5 points throughout the past six months and 140.9 points since the beginning of 2014, despite the most recent decline. A strong USD/Corn Exporter FX Index reduces the competitiveness of U.S. corn relative to other exporting regions (represented in green in the Global Corn Net Trade chart), ultimately resulting in less foreign demand, all other factors being equal. USD appreciation against the Argentine peso and Ukrainian hryvnia has accounted for the majority of the gains since the beginning of 2014.
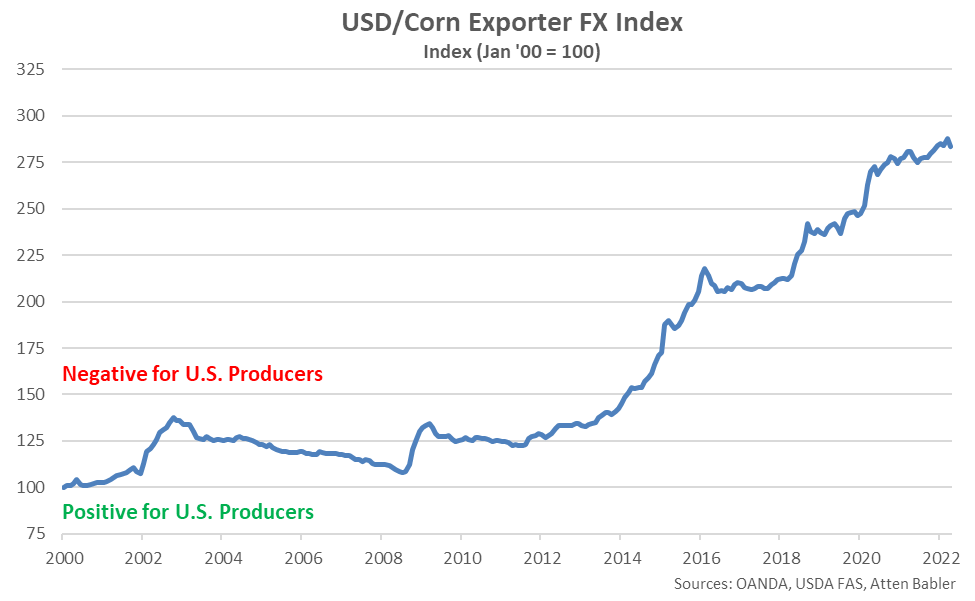
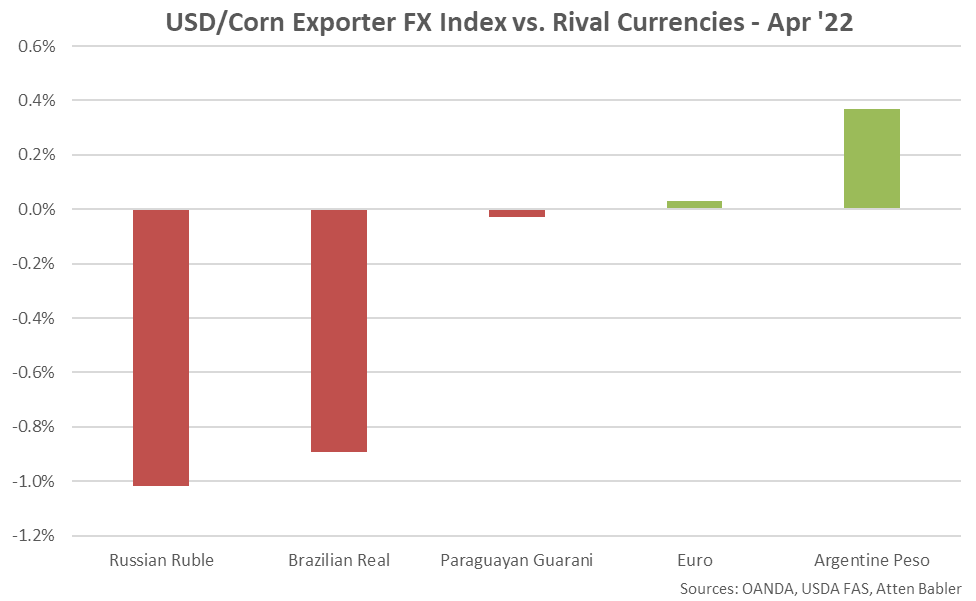
Appreciation against the USD within the USD/Corn Exporter FX Index during Apr ’22 was led by gains by the Russian ruble, followed by gains by the Brazilian real and Paraguayan guarani. USD gains were experienced against the Argentine peso and the euro.
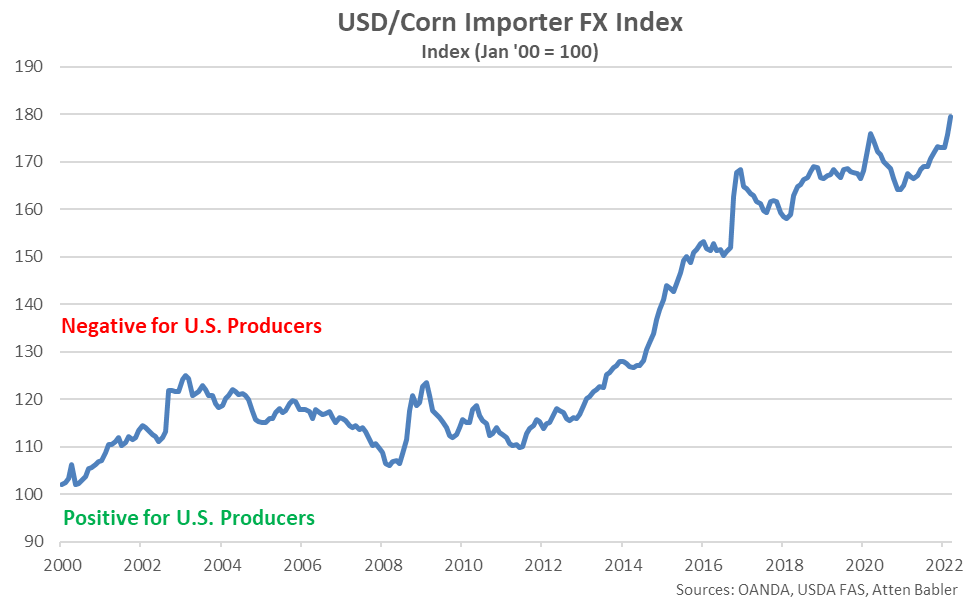
USD/Corn Importer FX Index:
The USD/Corn Importer FX Index increased 3.9 points throughout Apr ’22, reaching a record high value of 179.6. The USD/Corn Importer FX Index has increased 8.9 points throughout the past six months and 52.6 points since the beginning of 2014. A strong USD/Corn Importer FX Index results in less purchasing power for major corn importing countries (represented in red in the Global Corn Net Trade chart), making U.S. corn more expensive to import. USD appreciation against the Egyptian pound, Mexican peso, euro and Japanese yen has accounted for the majority of the gains since the beginning of 2014.
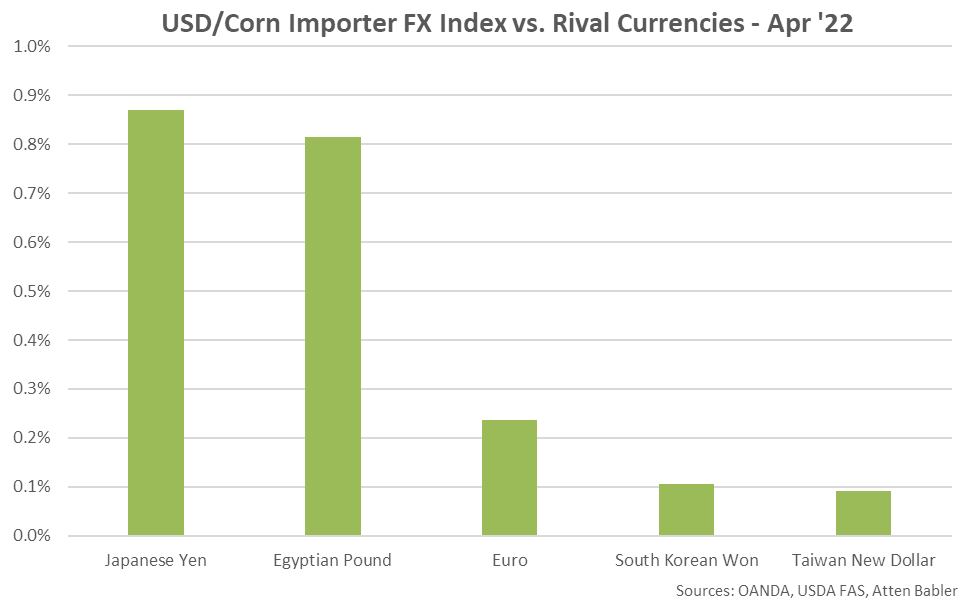
USD appreciation within the USD/Corn Importer FX Index during Apr ’22 was led by gains against the Japanese yen, followed by gains against the Egyptian pound, euro, South Korean won and Taiwan new dollar.
U.S. Corn Export Destinations:
Major destinations for U.S. corn are led by Japan, followed by Mexico, South Korea, Columbia, Egypt and China.
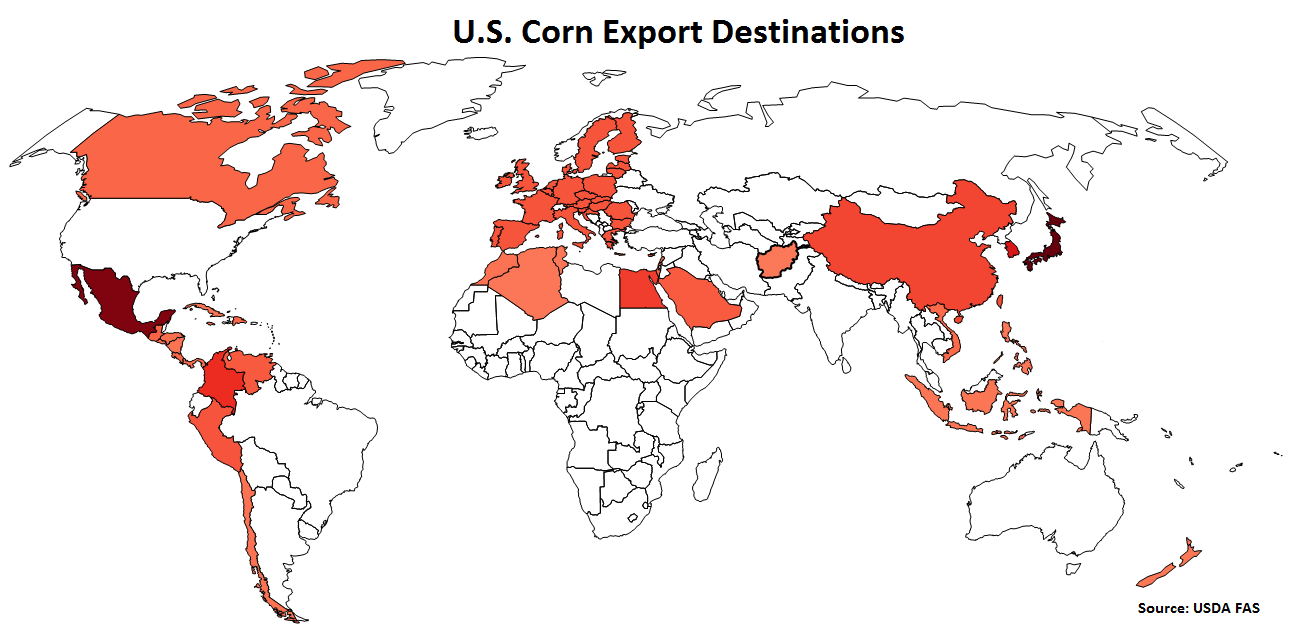
Japan accounts for 27% of the USD/Domestic Corn Importer FX Index, followed by Mexico at 24% and South Korea at 12%. Columbia, Egypt and China each account for between 5-10% of the index.
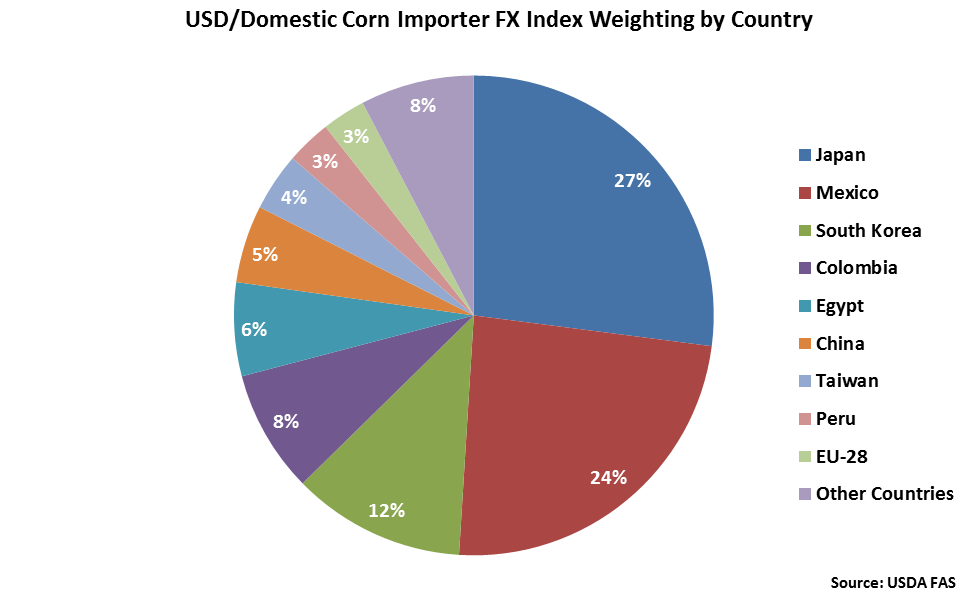
USD/Domestic Corn Importer FX Index:
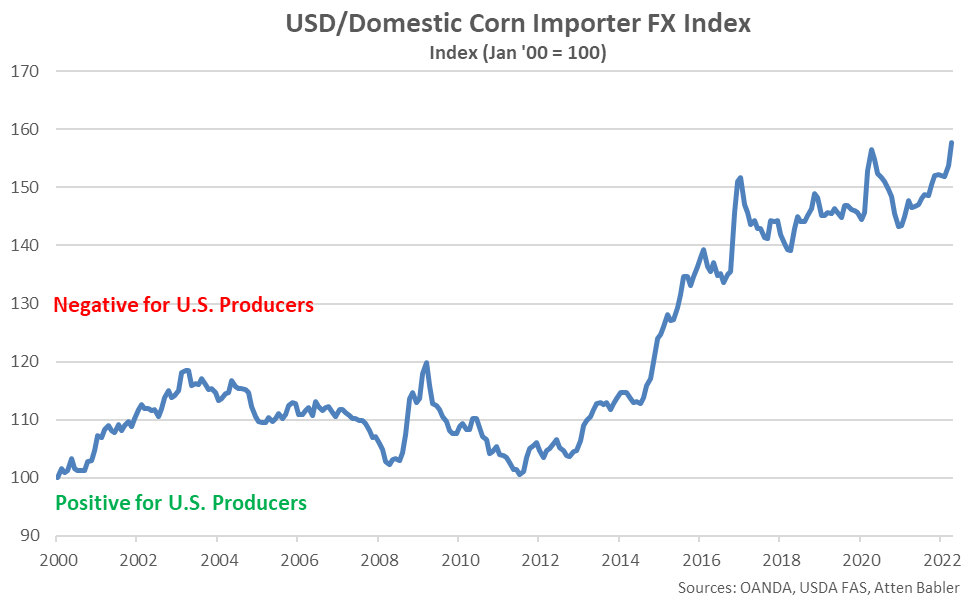
The USD/Domestic Corn Importer FX Index increased 3.9 points throughout Apr ’22, reaching a record high value of 157.7. The USD/Domestic Corn Importer FX Index has increased 7.2 points throughout the past six months and 44.1 points since the beginning of 2014. A strong USD/Domestic Corn Importer FX Index results in less purchasing power for the traditional buyers of U.S. corn (represented in red in the U.S. Corn Export Destinations chart), ultimately resulting in less foreign demand, all other factors being equal. USD appreciation against the Mexican peso and Japanese yen has accounted for the majority of the gains since the beginning of 2014.
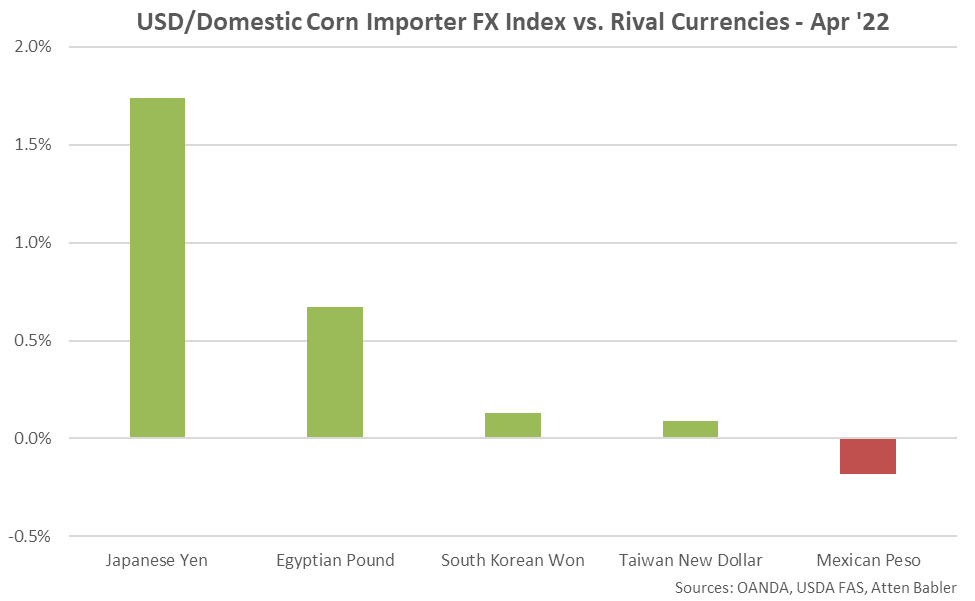
USD appreciation within the USD/Domestic Corn Importer FX Index during Apr ’22 was led by gains against the Japanese yen, followed by gains against the Egyptian pound, South Korean won and Taiwan new dollar. USD declines were exhibited against the Mexican peso.
Soybeans FX Indices:
The Atten Babler Commodities Soybeans Foreign Exchange (FX) Indices were mixed throughout Apr ’22. The USD/Soybean Exporter FX Index declined to a 25 month low level however the USD/Soybean Importer FX Index and USD/Domestic Soybean Importer FX Index each increased to 18 month high levels.
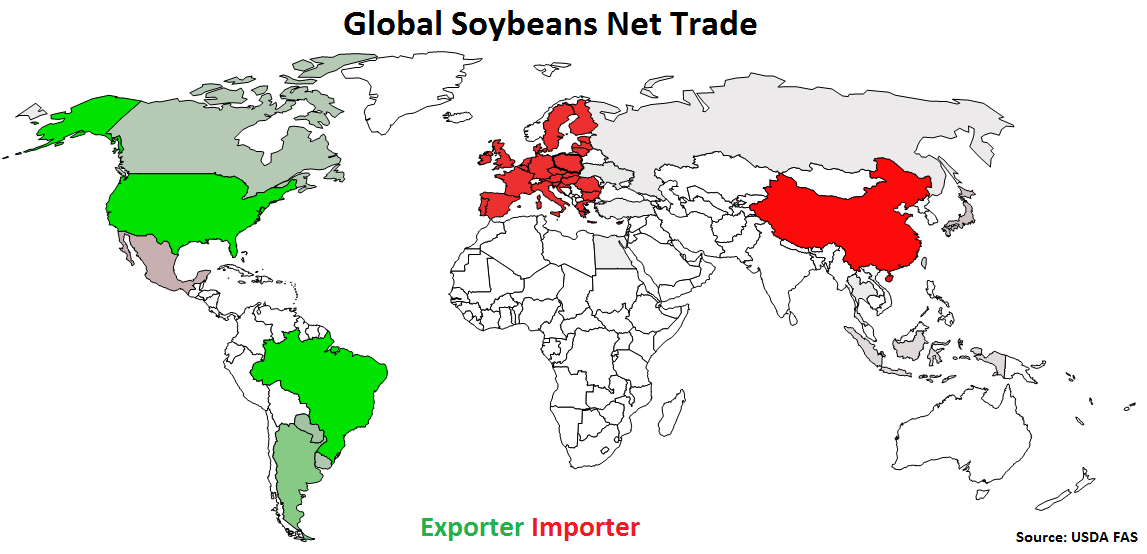
Global Soybeans Net Trade:
Major net soybeans exporters are led by Brazil, followed by the U.S., Argentina, Paraguay and Canada (represented in green in the chart below). Major net soybeans importers are led by China, followed by the EU-28, Mexico and Japan (represented in red in the chart below).
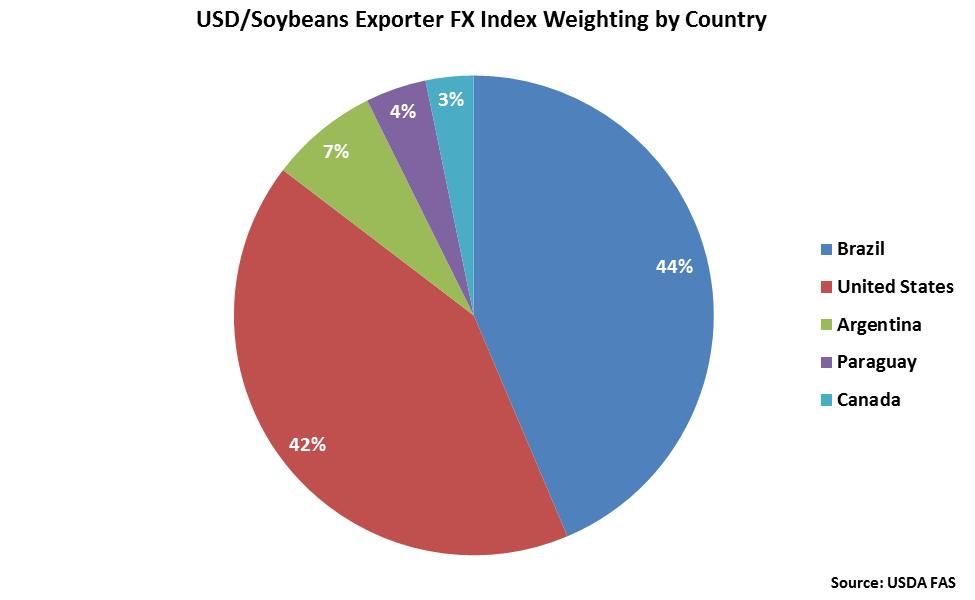
Brazil and the United States each account for over two fifths of the USD/Soybeans Exporter FX Index, followed by Argentina at 7%.
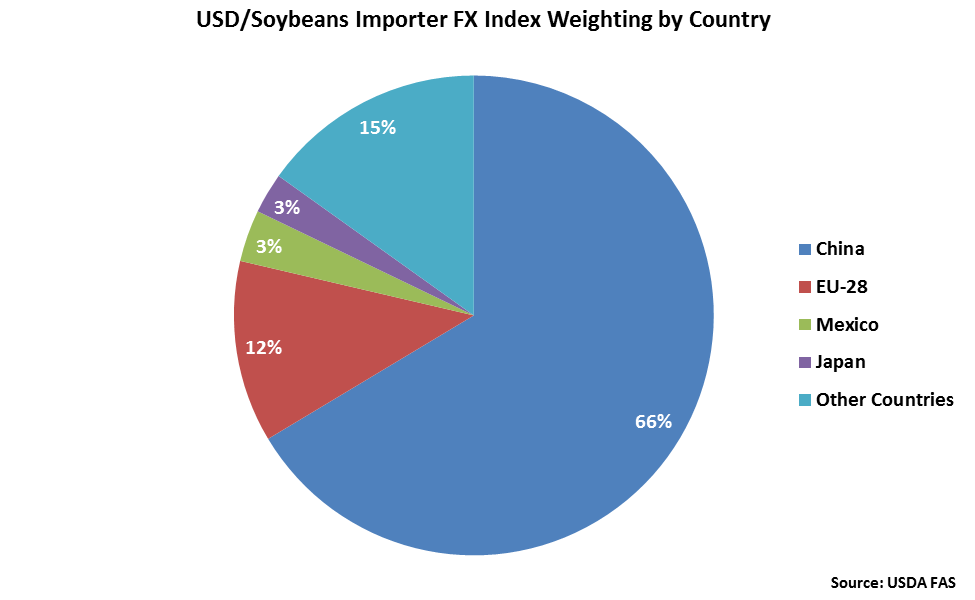
China accounts for nearly two thirds of the USD/Soybeans Importer FX Index, followed by the EU-28 at 12%.
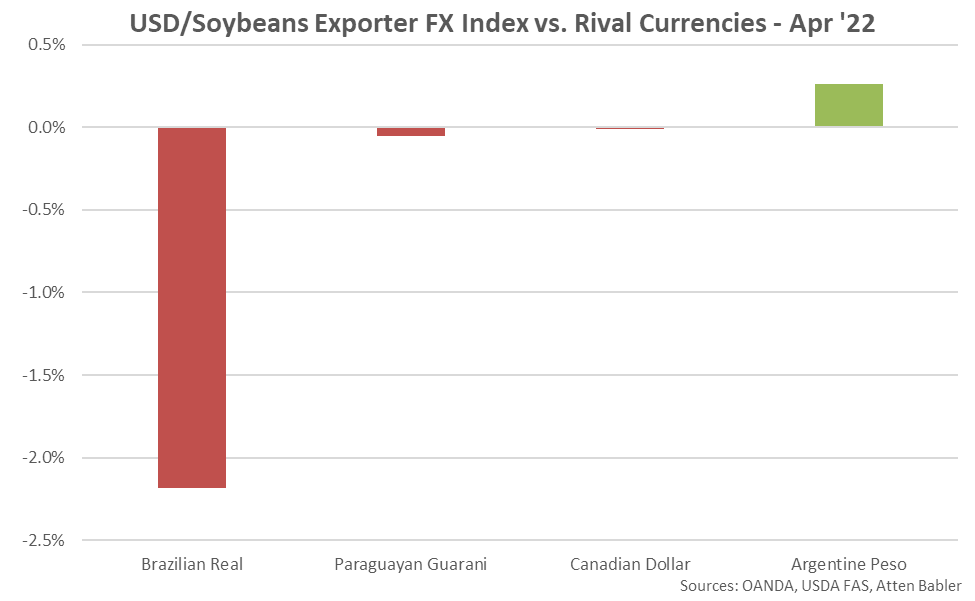
USD/Soybeans Exporter FX Index:
The USD/Soybeans Exporter FX Index declined 4.5 points throughout Apr ’22, finishing at a 25 month low value of 220.2. USD/Soybeans Exporter FX Index has declined 13.0 points throughout the past six months but remained up 91.9 points since the beginning of 2014, despite the most recent decline. A strong USD/Soybeans Exporter FX Index reduces the competitiveness of U.S. soybeans relative to other exporting regions (represented in green in the Global Soybeans Net Trade chart), ultimately resulting in less foreign demand, all other factors being equal. USD appreciation against the Brazilian real has accounted for the majority of the gains since the beginning of 2014.
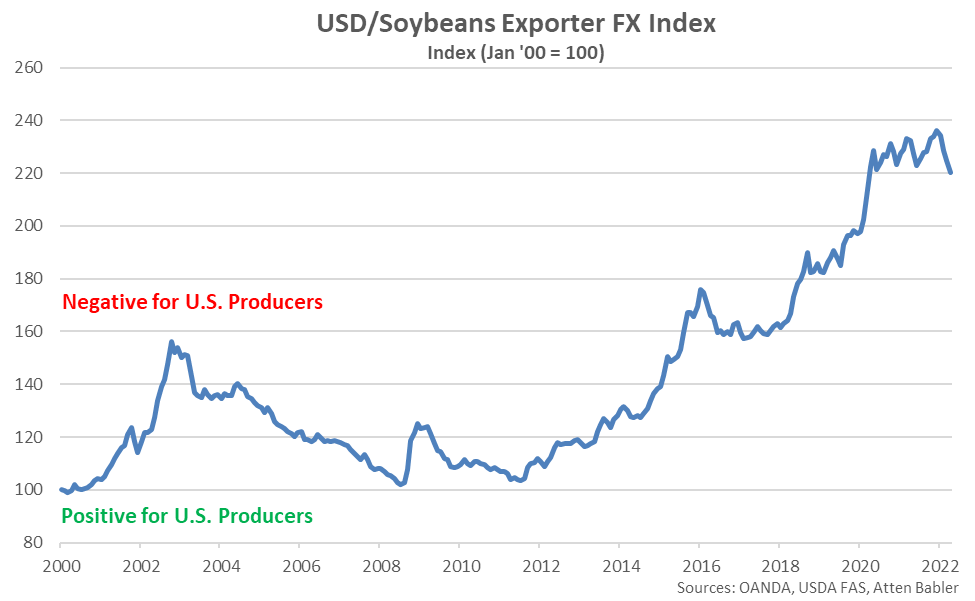
Appreciation against the USD within the USD/Soybeans Exporter FX Index during Apr ’22 was led by gains by the Brazilian real, followed by gains by the Paraguayan guarani and Canadian dollar. USD gains were experienced against the Argentine peso.
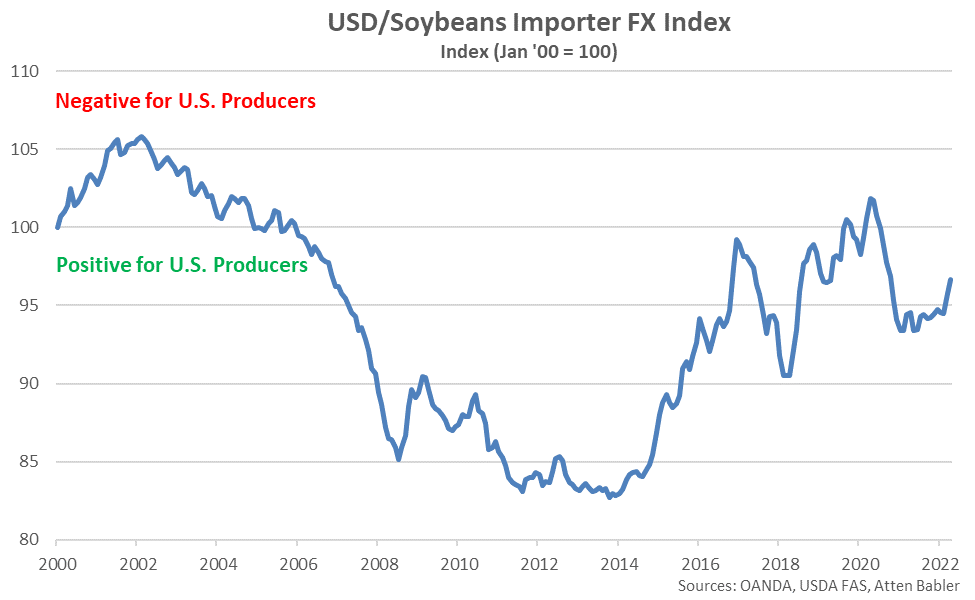
USD/Soybeans Importer FX Index:
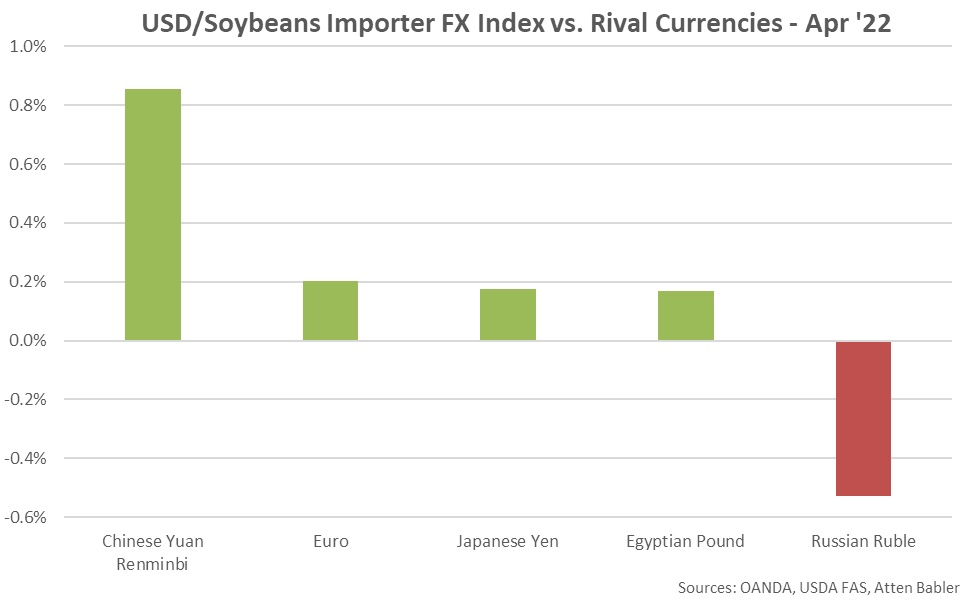
The USD/Soybeans Importer FX Index increased 0.9 points during Apr ’22, finishing at an 18 month high value of 96.7. The USD/Soybeans Importer FX Index has increased 2.4 points throughout the past six months and 13.9 points since the beginning of 2014. A strong USD/Soybeans Importer FX Index results in less purchasing power for major soybeans importing countries (represented in red in the Global Soybeans Net Trade chart), making U.S. soybeans more expensive to import. USD appreciation against the Chinese yuan renminbi has accounted for the majority of the gains since the beginning of 2014.
USD appreciation within the USD/Soybean Importer FX Index during Apr ’22 was led by gains against the Chinese yuan renminbi, followed by gains against the euro, Japanese yen and Egyptian pound. USD declines were exhibited against the Russian ruble.
U.S. Soybeans Export Destinations:
Major destinations for U.S. soybeans are led by China, followed by Mexico, Indonesia and Japan.
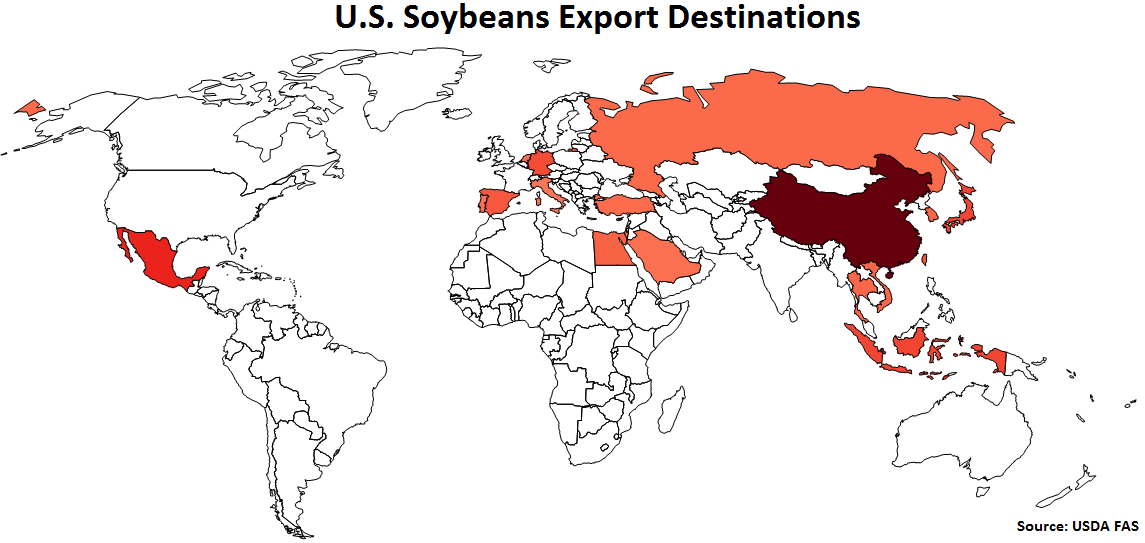
China accounts for nearly two thirds of the USD/Domestic Soybeans Importer FX Index. Mexico, Indonesia and Japan each account for between 5-10% of the index.
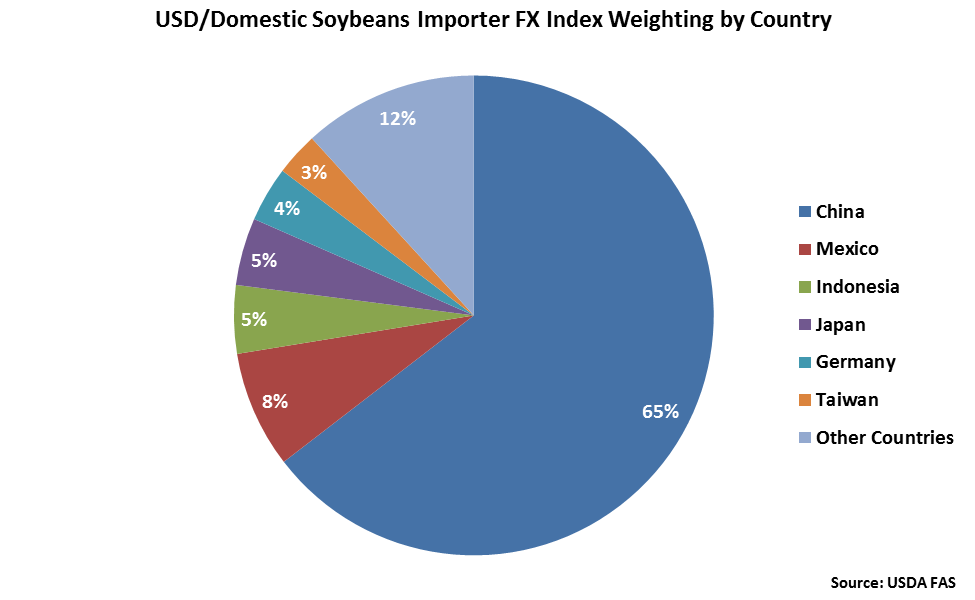
USD/Domestic Soybeans Importer FX Index:
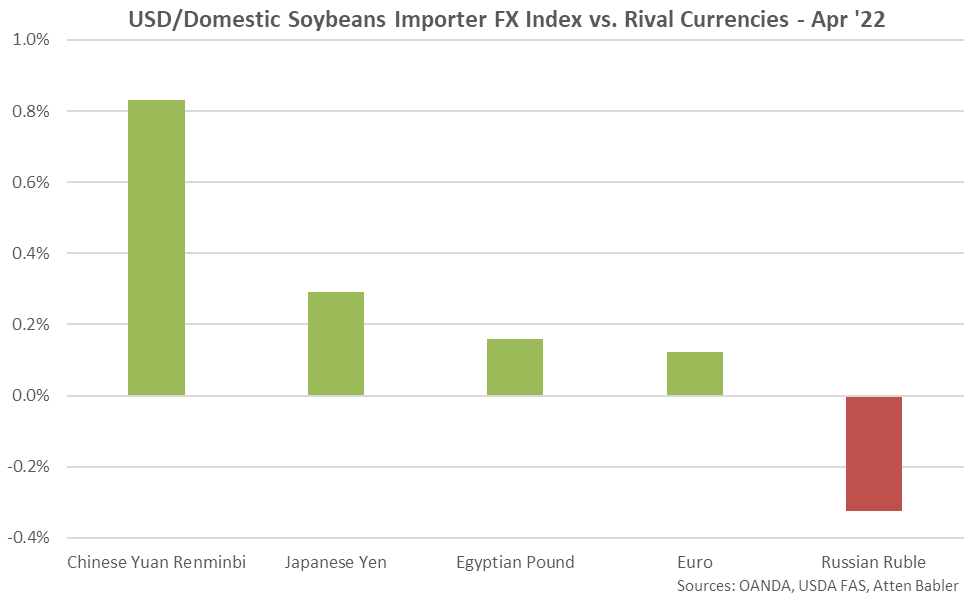
The USD/Domestic Soybeans Importer FX Index increased 1.1 points throughout Apr ’22, finishing at an 18 month high value of 99.4. The USD/Domestic Soybeans Importer FX Index has increased 2.1 points throughout the past six months and 13.9 points since the beginning of 2014. A strong USD/Domestic Soybeans Importer FX Index results in less purchasing power for the traditional buyers of U.S. soybeans (represented in red in the U.S. Soybeans Export Destinations chart), ultimately resulting in less foreign demand, all other factors being equal. USD appreciation against the Chinese yuan renminbi has accounted for the majority of the gains since the beginning of 2014.
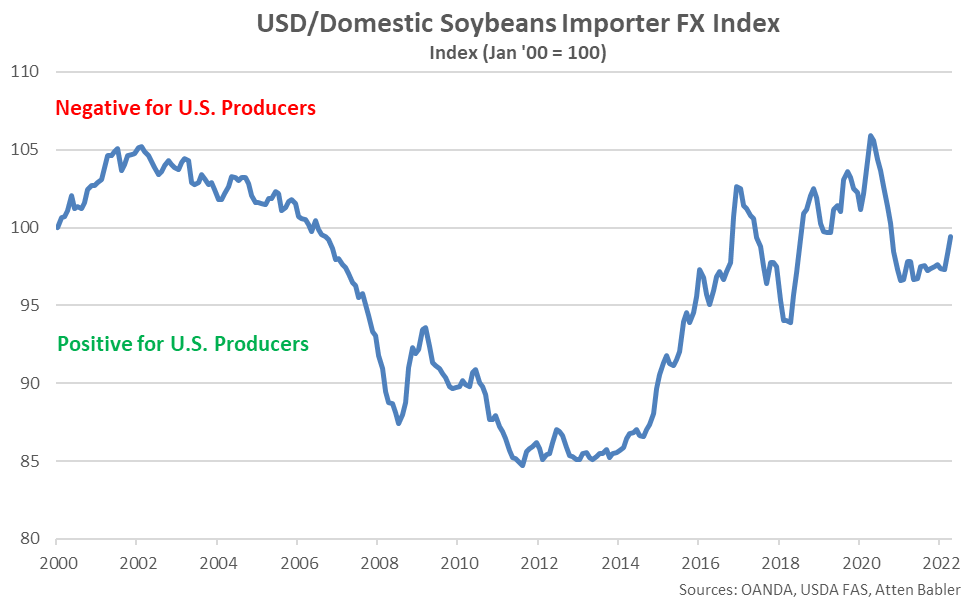
USD appreciation within the USD/Domestic Soybean Importer FX Index during Apr ’22 was led by gains against the Chinese yuan renminbi, followed by gains against the Japanese yen, Egyptian pound and euro. USD declines were exhibited against the Russian ruble.